Quick answer: what is contract management?
Contract management is the structured process of creating, executing, storing, monitoring and renewing contracts to ensure that every agreement delivers intended outcomes, risk is minimised, and compliance is maintained. AI-powered contract lifecycle management (CLM) platforms like Plexus now automate these workflows to improve visibility, speed and legal productivity across managing contracts, contractual obligations and contract performance.
TL;DR – what you'll learn in this guide
-
What contract management and contract lifecycle management really mean (with definitions)
-
How AI transforms effective contract management and contract administration
-
Differences between contract management software (CMS) and CLM (with comparison tables)
-
Best practices for managing contractual obligations and reducing legal risk
-
How Plexus supports legal, finance and operations teams across the organisation
-
FAQ answers to high-volume queries about contract performance and compliance
-
Visuals, summaries and checklists for fast reference on procurement and execution
Managing contracts in modern organisations & the role of contract management
-1.png?width=651&height=588&name=Untitled%20design%20(13)-1.png)
In modern organisations, contract management plays a critical role in guiding agreements through every stage of the contract lifecycle, from initial negotiation and execution to ongoing management, renewal, and closeout. Rather than being owned by a single role, effective management is a shared capability across legal, procurement, finance, sales, and operational teams.
When managed well, contracts are not just executed efficiently, but actively monitored and optimised to deliver maximum commercial value while minimising legal, financial, and compliance risk.
Core responsibilities of contract management
At its core, contract management ensures that contractual obligations are clearly defined, understood, and met throughout the life of an agreement. This includes maintaining compliance with relevant regulations, internal policies, and governance frameworks, while ensuring contracts align with broader organisational objectives.
Modern management involves contract administration, performance monitoring, and proactive oversight to identify issues early. By embedding governance and accountability into contract processes, organisations reduce risk and ensure all parties — internal and external — fulfil their responsibilities.
Capabilities required for effective contract management
Successful contract management depends on a combination of commercial, legal, and operational capabilities. Organisations must be able to analyse complex contracts, identify potential risks, and implement strategies to mitigate exposure across the lifecycle.
Strong communication and collaboration are essential, enabling teams to align legal requirements with commercial goals. Negotiation, stakeholder management, and risk assessment all contribute to ensuring contracts are not only compliant, but commercially sound and fit for purpose.
Contract management in complex and high-risk environments
In complex or high-stakes environments — such as construction projects, infrastructure programs, or heavily regulated industries — the role of contract management becomes even more critical. Contracts in these settings often involve multiple parties, evolving scopes, and significant financial exposure.
Effective contract management helps organisations ensure obligations are met, timelines are maintained, and budgets are controlled. A proactive approach enables teams to identify issues early, manage variations, and prevent disputes, delays, and compliance failures before they escalate.
Governance, administration, and performance oversight
Contract management is also central to maintaining strong governance and administrative discipline. This includes establishing consistent processes for contract approval, execution, amendment, and renewal, ensuring agreements are managed in line with organisational standards and best practices.
Ongoing performance monitoring allows organisations to assess whether contracts are delivering expected outcomes. This visibility enables continuous improvement, supports renegotiation where appropriate, and helps identify cost-saving or value-creation opportunities.
Risk management and strategic impact
Risk identification and mitigation sit at the heart of effective contract management. By analysing contractual terms, obligations, and dependencies, organisations can surface potential legal, financial, and operational risks early and take action to address them.
This strategic oversight helps reduce the likelihood of disputes, financial losses, and reputational damage, while enabling leadership teams to make informed decisions based on accurate contract data and insights.
Enabling cross-functional collaboration
Modern management of the process depends on close collaboration across legal, finance, procurement, sales, and operational teams. Clear visibility into contracts and obligations ensures stakeholders are aligned and able to act quickly when circumstances change.
By translating complex contractual requirements into clear, actionable insights, contract management supports faster decision-making and stronger alignment between legal compliance and business execution.
Delivering organisational value through contracts
Ultimately, the role of contract management is to ensure contracts deliver their intended value — whether through cost control, risk reduction, improved supplier performance, or faster deal execution — while maintaining compliance with all relevant regulations.
When approached strategically, contract management shifts from an administrative burden to a source of competitive advantage, enabling organisations to operate with greater confidence, agility, and control in an increasingly complex business environment.
Understanding contract management and CLM
What is contract management?
Contract management encompasses the end-to-end processes involved in creating, executing, analysing and managing contracts with suppliers, partners and customers. At its core, effective contract management ensures that all parties fulfil their contractual obligations, reduces legal risk, and maximises the value delivered through agreements.
For legal departments and business teams, managing contracts effectively means maintaining control over every agreement from initial briefing through execution, ongoing monitoring of contract performance, and ultimately renewal or termination. The focus is on ensuring compliance with relevant regulations whilst delivering business value and managing relationships with key stakeholders.
Good contract management requires both strategic oversight and operational discipline. Contract managers need specific skills in negotiation, project coordination, legal analysis, and financial oversight to identify potential issues before they escalate, monitor performance against agreed terms, and ensure resources are deployed effectively throughout the contract lifecycle.
What is contract lifecycle management (CLM)?
Contract lifecycle management (CLM) refers to the systematic approach of managing contracts from initial request through drafting, negotiation, approval, execution, compliance monitoring, and renewal. CLM platforms provide technology infrastructure that automates and streamlines these processes, giving organisations better visibility, control and insights across their entire contract portfolio.
Modern CLM software transforms contract administration by centralising all agreements in a single repository, automating routine tasks like contract drafting and approval workflows, and providing analytics to track key obligations, deadlines and performance metrics. This enables legal teams to focus on strategic work rather than manual contract management processes.
For organisations managing high volumes of contracts across multiple departments, CLM technology delivers measurable benefits: faster contract execution, reduced legal bottlenecks, improved compliance, and enhanced visibility into contractual commitments. It supports both the legal department and business users who need access to contract information to make informed decisions.
According to industry research, organisations implementing CLM solutions typically see 65% improvements in legal productivity, 90% faster contract execution times, and 70% reduction in time spent on routine contract administration tasks. These efficiency gains allow in-house legal teams to double their impact without increasing headcount.
Contract management vs CLM (with table)
Whilst the terms are often used interchangeably, there are important distinctions between contract management as a discipline and contract lifecycle management as a technology-enabled approach. Understanding these differences helps organisations choose the right tools and strategies for their specific needs.
Key Differences:
|
Aspect
|
Contract Management
|
CLM
|
|
Definition
|
The discipline and practices of managing contracts
|
Technology platform that automates the contract lifecycle
|
|
Focus
|
People, processes, responsibilities
|
Automation, workflows, analytics
|
|
Scope
|
All activities related to contracts
|
End-to-end digital contract workflow
|
|
Implementation
|
Can be manual or technology-assisted
|
Requires software platform
|
|
Key Users
|
Contract managers, legal teams, procurement
|
Legal ops, business users, finance teams
|
|
Primary Benefits
|
Clear responsibilities and control
|
Speed, efficiency, visibility, compliance
|
Contract management software (CMS) typically focuses on storage and basic organisation of executed agreements, whilst CLM platforms handle the entire lifecycle including creation, negotiation, approval workflows, obligation management, and renewal processes. For growing organisations, CLM represents a comprehensive solution that supports good contract management practices with powerful automation and AI capabilities.
What happens after a contract is signed?
"A signed contract that isn't managed is a risk waiting to surface."
Contract execution marks the beginning, not the end, of effective contract management. Once agreements are signed, organisations must actively monitor contract performance, track key dates and obligations, manage ongoing relationships, and ensure compliance with all terms.
Post-execution contract management involves storing agreements securely, setting up monitoring for critical milestones and renewal dates, tracking deliverables against agreed standards, managing any variations or amendments, and maintaining clear communication channels with suppliers, partners or customers. Financial teams need visibility into payment schedules and budget implications, whilst legal departments must monitor for compliance with relevant regulations and internal policies.
Without proper post-execution management, organisations expose themselves to significant legal risk: missed renewal opportunities, unmet contractual obligations, cost overruns, non-compliance with regulatory requirements, and damaged business relationships. Effective contract lifecycle management ensures nothing falls through the cracks by providing automated alerts, centralised obligation tracking, and comprehensive reporting across the entire contract
The contract lifecycle – step-by-step

Understanding each phase of the contract lifecycle helps organisations identify where bottlenecks occur, where risk accumulates, and where automation delivers the greatest value. Here's how modern contract management supports each stage:
Briefing (intake)
The contract lifecycle begins when a business team identifies the need for an agreement. This intake phase captures essential information: what services or products are needed, who the counterparty is, what the commercial terms should be, what risks need to be addressed, and what the timeline is for execution.
Effective intake processes use standardised request forms that route to the appropriate legal resources, triage simple requests to self-service templates whilst escalating complex agreements to senior lawyers, and provide immediate visibility into the pipeline of work. AI-powered CLM platforms can automatically classify request types, suggest relevant templates, and even pre-populate contract terms based on previous similar agreements.
Poor intake management creates immediate bottlenecks. When business teams submit incomplete or unclear requests, legal departments waste time gathering basic information. When there's no central intake system, requests arrive via email, Slack, or casual conversations, making it impossible to track workload or prioritise effectively. Modern CLM software solves these challenges with structured intake workflows that capture all necessary information upfront.
Drafting
Contract drafting translates business requirements into legally enforceable terms. This phase requires balancing commercial objectives with risk management, ensuring compliance with relevant laws and regulations, incorporating company-standard provisions, and creating clear language that all parties can understand.
Traditional drafting is time-intensive: lawyers start from previous contracts, manually adapt language for new circumstances, cross-reference internal playbooks, and coordinate with various stakeholders. AI contract management tools revolutionise this process by offering intelligent template libraries that automatically populate based on deal parameters, clause libraries with pre-approved language for common scenarios, and real-time suggestions drawn from your organisation's best practices.
For legal teams managing high contract volumes, automated drafting capabilities can reduce drafting time by 60-80%. Rather than spending hours on routine agreements, lawyers focus their skills on complex negotiations and strategic advice. The technology ensures consistency across your contract portfolio whilst maintaining the flexibility to customise for specific business needs.
Negotiation
Contract negotiation involves multiple rounds of redlines, comments, and discussions between parties. This phase tests relationships, clarifies expectations, and determines the final risk allocation. Effective negotiation requires understanding the other party's interests, knowing which terms are negotiable versus mandatory, maintaining version control across multiple drafts, and documenting decisions for future reference.
Managing negotiation manually creates several pain points: version confusion when multiple stakeholders edit documents simultaneously, lost negotiation history when discussions happen across emails and meetings, delays when redlines require manual review and legal analysis, and missed opportunities to learn from previous negotiations with similar counterparties.
Modern CLM platforms streamline negotiation with collaborative redlining tools, automated version control that tracks every change, AI-powered clause analysis that flags non-standard or risky terms, playbook integration that helps business users understand which changes are acceptable, and detailed audit trails that document every decision. This infrastructure accelerates negotiation whilst improving risk management.
Approval
Before execution, contracts typically require multiple approvals based on factors like contract value, risk level, counterparty type, and term length. Approval workflows ensure appropriate oversight, prevent unauthorised commitments, incorporate necessary sign-offs from finance, procurement, privacy, or other relevant departments, and maintain audit trails for compliance purposes.
Manual approval processes are notoriously slow and opaque. Contracts sit in email inboxes waiting for responses, stakeholders don't know where agreements are stuck, urgent deals miss critical deadlines, and there's no systematic way to enforce approval policies. These bottlenecks frustrate business teams and cost real money in missed opportunities.
Automated approval workflows eliminate these delays by routing contracts automatically based on predefined rules, sending automatic reminders to approvers, providing real-time status visibility to all stakeholders, and escalating when approvals exceed time limits. AI can even pre-identify approval requirements based on contract terms, ensuring the right people review at the right time. The result is 70-90% faster approval times and far less frustrated business partners.
Execution
Contract execution formalises the agreement through signatures from all parties. In today's digital environment, this phase increasingly uses electronic signatures that are legally valid, provide strong audit trails, integrate with contract management systems, and dramatically accelerate the signing process compared to printing, scanning, and mailing paper contracts.
Modern CLM platforms integrate with leading e-signature providers to create seamless execution workflows: contracts flow directly from approval to signing, signers receive automated reminders if they haven't completed signatures, the platform tracks signature status in real-time, and fully executed agreements automatically route to the repository for storage. This integration eliminates manual handoffs and ensures executed contracts are immediately accessible to those who need them.
Post-execution, the platform automatically extracts key terms and metadata, sets up obligation tracking and renewal alerts, notifies relevant stakeholders that the agreement is live, and ensures the contract is properly filed for easy future retrieval. This seamless handoff from execution to ongoing management prevents the common scenario where signed contracts disappear into email archives.
Storage & obligation management
Once executed, contracts must be stored securely and their key terms actively managed. This phase involves maintaining a centralised, searchable repository of all agreements, tracking critical dates like renewal deadlines, payment milestones, or termination windows, monitoring ongoing obligations such as deliverables, reporting requirements, or compliance duties, and managing any amendments, extensions, or variations that occur during the contract term.
Many organisations still manage contracts in disconnected systems: executed agreements in shared drives, key dates in Excel spreadsheets, obligations tracked in someone's memory. This fragmentation creates serious risks. When renewal dates pass unnoticed, organisations lose negotiating leverage or get locked into unfavourable automatic renewals. When obligations aren't tracked systematically, companies breach agreements without realising it. When contracts aren't searchable, teams can't answer basic questions about what they've committed to.
Modern CLM platforms solve these challenges by providing a single source of truth for all contract data, using AI to automatically extract key terms, obligations, and dates, setting up automated alerts well before critical deadlines, enabling powerful search across all agreements, and providing dashboards that show portfolio-wide insights. This visibility transforms contract management from reactive firefighting to proactive risk management.
Renewal
Contract renewal represents both risk and opportunity. Organisations must decide whether to renew, renegotiate, or terminate agreements based on factors like supplier performance, changing business needs, market conditions, regulatory changes, and budget constraints. Effective renewal management requires reviewing contracts well before expiration dates, analysing whether terms remain favourable, coordinating with stakeholders about continuation needs, and either initiating renegotiation or managing smooth transition to alternative suppliers.
Without systematic renewal management, organisations frequently miss optimal renegotiation windows. By the time they realise a contract is expiring, they lack leverage to negotiate better terms and may be forced into unfavourable automatic renewals simply because there's insufficient time to find alternatives. This costs money and perpetuates suboptimal relationships.
AI-powered CLM platforms transform renewal management by providing early visibility into upcoming renewals across the entire portfolio, automatically flagging contracts that may need renegotiation based on spend levels or poor performance, analysing whether renewal terms remain market-competitive, and streamlining the renewal workflow so decisions get made promptly. This proactive approach helps organisations optimise their contract portfolio continuously.
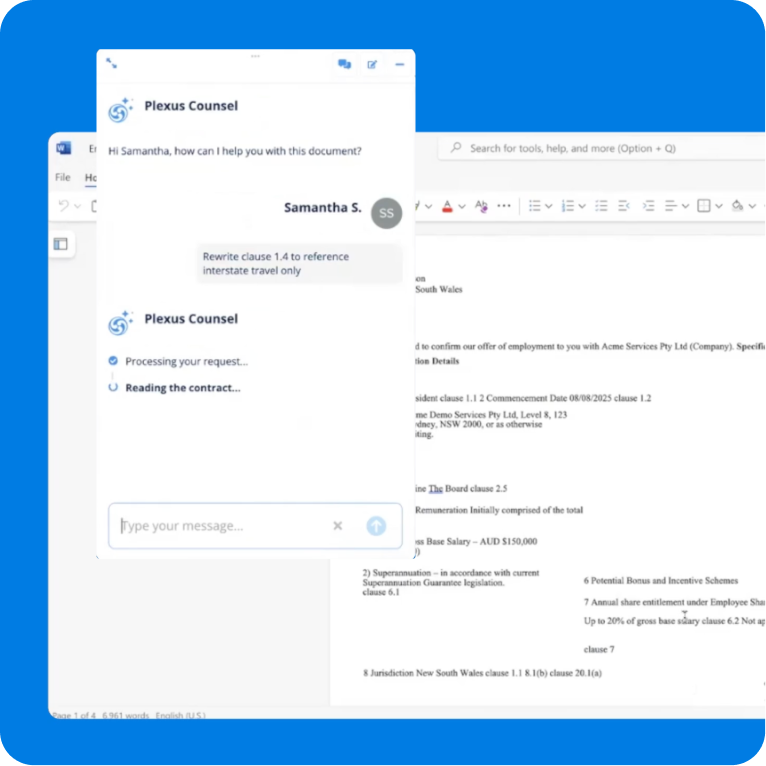
AI in contract management
What is AI contract management?
AI contract management refers to the application of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies to automate, enhance, and optimise contract lifecycle processes. Unlike traditional contract management software that simply stores and organises agreements, AI-powered platforms actively analyse contract language, extract key terms automatically, identify risks and anomalies, provide intelligent recommendations, and continuously learn from your organisation's contract data.
The most impactful AI applications in contract management include natural language processing (NLP) to understand and analyse contract text, machine learning to identify patterns and provide insights, automated clause extraction to pull key terms without manual review, risk analysis that flags non-standard or problematic provisions, and intelligent search that understands context and intent, not just keywords.
For legal teams drowning in contract volumes, AI represents transformational value. Tasks that previously required hours of manual review—extracting payment terms from 500 supplier agreements, identifying contracts with specific indemnity clauses, or analysing renewal dates across your portfolio—now happen in seconds. This frees lawyers to focus on high-value strategic work whilst ensuring nothing important gets missed.
AI-powered review, drafting & negotiation
AI-powered contract review analyses agreements against your playbook and flags provisions that deviate from approved terms, identifies missing clauses that should be included, highlights unusual or risky language that warrants legal attention, and provides specific redline suggestions to bring contracts into compliance with your standards. This accelerates review cycles by 60-80% whilst improving consistency and reducing risk.
For contract drafting, AI systems suggest optimal clause language based on deal parameters, automatically populate templates with appropriate terms, identify internal precedents from similar successful agreements, and adapt language based on counterparty type, jurisdiction, or risk profile. Rather than starting each contract from scratch, lawyers work from intelligent first drafts that capture institutional knowledge.
During negotiation, AI tools analyse counterparty positions in real-time, compare proposed terms against your historical acceptance rates, predict likely negotiation outcomes based on previous similar deals, and provide data-driven recommendations about which points to push and which to concede. This intelligence helps negotiators achieve better outcomes whilst moving deals forward efficiently.
End-to-end CLM with AI workflow automation
Modern AI-powered CLM platforms don't just help with individual tasks—they orchestrate entire workflows intelligently. The system automatically routes contracts to appropriate reviewers based on contract type, value, risk score, and other factors, adapts approval requirements dynamically if flagged risks require additional oversight, provides each stakeholder with contextual information relevant to their review, and escalates automatically when workflows stall to prevent bottlenecks.
This intelligent automation extends beyond approvals. AI can trigger follow-up actions when specific contract milestones are reached, coordinate cross-functional teams that need to collaborate on deliverables, generate automatic reports for stakeholders about contract status, and even initiate renewal conversations at optimal times based on historical patterns.
The result is a contract management infrastructure that operates more like an intelligent assistant than traditional software. Rather than simply storing contracts, the platform actively manages workflows, prevents problems before they occur, and ensures your organisation captures maximum value from every agreement. Legal teams report that AI-powered workflow automation reduces administrative burden by 70% whilst improving compliance and visibility.
AI contract risk analysis & insights
AI risk analysis continuously monitors your contract portfolio for potential issues. The technology identifies contracts with high financial exposure, flags agreements nearing critical compliance dates, highlights suppliers or customers with problematic contract terms, detects patterns that indicate increased risk, and alerts relevant stakeholders before problems escalate.
Beyond individual contract risk, AI provides portfolio-level insights that were previously impossible to obtain. Which contract types carry the highest risk? Which suppliers consistently negotiate better terms? Where are we exposed to regulatory compliance issues? What's our total financial obligation across all active agreements? These strategic insights help general counsel and finance teams make informed decisions about contract strategy, resource allocation, and risk management priorities.
AI contract summaries represent another powerful application. Rather than requiring stakeholders to read entire contracts, AI generates concise summaries that highlight key terms, obligations, financial commitments, and risk factors. This democratises contract knowledge across the organisation, enabling faster decision-making whilst ensuring critical information doesn't get overlooked.
.png?width=651&height=588&name=Untitled%20design%20(16).png)
Do you need CLM or CMS?
The decision between basic contract management software (CMS) and comprehensive contract lifecycle management platforms depends on your organisation's contract volumes, complexity, and strategic objectives. Understanding the distinction helps ensure you invest in technology that delivers appropriate value.
Contract management software typically provides document storage, basic search capabilities, simple metadata tagging, and manual workflow support. These systems work adequately for organisations with low contract volumes, minimal compliance requirements, straightforward agreement types, and limited cross-functional coordination needs. If your primary need is simply organising and finding executed contracts, CMS may suffice.
However, organisations managing significant contract volumes, complex compliance requirements, high-value or high-risk agreements, or extensive supplier and customer portfolios typically require comprehensive CLM platforms. These systems provide end-to-end lifecycle management from intake through renewal, intelligent automation that reduces manual work, AI-powered analysis and risk management, sophisticated reporting and analytics, and seamless integration with other business systems.
According to the ACC Legal Operations Maturity Model, mature legal operations teams leverage technology platforms that support strategic contract management, not just document storage. For growing organisations, CLM represents infrastructure investment that scales with your business and delivers compounding returns through improved efficiency, reduced risk, and better business outcomes.
Key CLM features to look for
When evaluating contract lifecycle management platforms, focus on capabilities that address your organisation's specific pain points whilst providing room to grow. Essential features include:
Intake and request management: Structured intake workflows that capture requirements upfront, automated routing based on contract type and complexity, self-service options for routine agreements, and clear visibility into the legal department's workload and priorities.
Intelligent contract drafting: Template libraries with approved standard language, automated clause assembly based on deal parameters, integration with your legal playbook, and version control that tracks all changes throughout the drafting process.
Collaborative review and negotiation: Real-time collaboration tools for internal stakeholders, redlining capabilities that integrate with Microsoft Word, automated version comparison, clause-level commenting, and detailed audit trails that document every decision.
Workflow and approval automation: Configurable approval workflows based on contract attributes, automated routing to appropriate stakeholders, escalation when approvals exceed time limits, and electronic signature integration for seamless execution.
AI-powered analysis: Automated extraction of key terms and metadata, risk scoring that flags non-standard provisions, clause library that identifies and categorises contract language, and intelligent search that understands context and intent.
Obligation and deadline management: Automated extraction of key dates and commitments, proactive alerts before critical deadlines, obligation tracking throughout the contract term, and automated renewal management workflows.
Repository and search: Centralised storage for all contracts and related documents, powerful search across contract text and metadata, role-based access controls, and comprehensive audit trails for compliance purposes.
Analytics and reporting: Portfolio-level dashboards showing key metrics, custom reports for different stakeholders, spend analysis and contract value tracking, and cycle time analytics that identify bottlenecks.
Integration capabilities: Seamless connections with CRM systems like Salesforce, ERP platforms for financial data, procurement systems, e-signature providers, and other relevant business applications.
Leading platforms like Plexus provide these capabilities in modular, scalable configurations that grow with your organisation's needs.
Cloud vs on-premise CLM
The deployment model for your CLM platform significantly impacts implementation timelines, total cost of ownership, security considerations, and ongoing maintenance requirements. Understanding the trade-offs helps organisations make informed decisions.
Cloud-based CLM solutions have become the preferred choice for most organisations. These platforms offer rapid deployment with minimal IT infrastructure requirements, automatic updates that ensure you always have the latest features, elastic scalability that grows with your contract volumes, lower upfront costs with subscription-based pricing, and vendor-managed security and compliance. Cloud solutions enable faster time-to-value, particularly for organisations without extensive internal IT resources.
On-premise CLM platforms may still make sense for organisations with strict data residency requirements, regulatory constraints that prohibit cloud storage of sensitive contract data, substantial existing infrastructure investments, or very specific customisation needs. However, on-premise solutions require significant upfront capital investment, dedicated IT resources for maintenance and updates, longer implementation timelines, and more complex upgrade processes.
For most growing organisations, cloud-based CLM delivers superior value. The deployment model allows legal teams to focus on contract management rather than IT infrastructure, ensures continuous improvement through regular platform updates, and provides the flexibility to scale up or down based on business needs. When evaluating cloud providers, examine their security certifications, data backup procedures, disaster recovery capabilities, and compliance with relevant industry standards.
Evaluating AI capabilities
Not all AI-powered contract management platforms deliver equal value. When evaluating vendors' AI capabilities, look beyond marketing claims to understand what the technology actually does and how it will impact your workflows.
Transparency and explainability: Can the system explain why it flagged a particular clause as risky? Does it show what data informed its recommendations? AI that operates as a black box creates compliance concerns and reduces user trust. Look for platforms that provide clear reasoning for their analyses.
Training and adaptation: How does the AI learn from your specific contracts and preferences? Systems that rely solely on generic training data may miss nuances specific to your industry, jurisdiction, or risk tolerance. The best platforms continuously learn from your organisation's contract data and user feedback to improve accuracy over time.
Accuracy and reliability: What's the platform's accuracy rate for extracting key terms? How often does it miss critical clauses or misclassify contract language? Request metrics on performance, and ask for trial periods to test accuracy with your actual contracts before committing.
Practical value: Does the AI address genuine pain points in your workflows, or is it technology for technology's sake? Focus on capabilities that demonstrably reduce manual work, improve risk management, or accelerate contract cycles. Features like AI contract review, automated metadata extraction, and intelligent search typically deliver the most immediate value.
Data security and privacy: How does the vendor use your contract data to train AI models? Are your contracts kept confidential from other customers? What safeguards prevent sensitive information from being exposed? These questions are critical for protecting confidential business information and maintaining client trust.
Industry analysts at Gartner evaluate CLM vendors based on their vision for AI integration and execution capabilities. Reviewing independent analyst reports provides valuable perspective on which vendors lead in AI innovation versus those making aspirational claims.
Implementation considerations
Successful CLM implementation requires more than selecting the right technology. Organisations must plan carefully for change management, data migration, process redesign, and ongoing adoption to realise the platform's full value.
Change management: CLM platforms disrupt established workflows and require new ways of working. Successful implementations invest heavily in stakeholder communication about why change is necessary, comprehensive training for all user groups, ongoing support as teams adapt, and clear processes for requesting enhancements or reporting issues. Resistance to change represents the primary reason CLM projects fail to deliver expected value.
Data migration: Moving existing contracts into a new platform involves extracting documents from current storage locations, cleansing and standardising contract metadata, prioritising which contracts to migrate first, and validating that critical information transferred correctly. Organisations often underestimate this effort. Starting with recent high-value contracts and migrating historical agreements progressively works better than attempting to migrate everything simultaneously.
Process redesign: CLM platforms enable better processes, but only if organisations redesign workflows to leverage platform capabilities. Simply replicating manual processes in software delivers minimal value. Work with business stakeholders to identify bottlenecks and pain points, design streamlined workflows that eliminate unnecessary steps, establish clear roles and responsibilities, and define metrics to measure improvement.
Integration planning: CLM delivers maximum value when integrated with other business systems. Contract data should flow seamlessly to finance for budget tracking, sales for customer relationship management, procurement for supplier management, and other relevant departments. Plan these integrations thoughtfully based on priority business needs rather than trying to integrate everything immediately.
Phased rollout: Implementing CLM across the entire organisation simultaneously creates overwhelming complexity. More successful approaches involve starting with a specific contract type or department, proving value and refining processes with early adopters, learning from initial challenges before broader deployment, and gradually expanding functionality and user base. This reduces risk whilst building organisational confidence.
Real-world examples like ENGIE Australia's contract management transformation demonstrate how organisations successfully implement CLM to achieve measurable business outcomes. Studying case studies from similar organisations provides valuable insights into realistic timelines, common challenges, and effective practices.
.png?width=600&height=160&name=CUSTOMER%20NEWS%20Archtop%20Fibers%20Digital%20Construction%20Success%20with%20Render%20(6).png)
Plexus AI for contract management

How Plexus supports the full contract lifecycle
Plexus positions itself as the future-facing legal operating system: an AI-powered platform that centralises all legal work—contracts, matter management, compliance, reporting—so that in-house legal and marketing teams can operate faster, smarter and with confidence. Unlike point solutions that address only contract management, Plexus provides comprehensive infrastructure that supports legal teams' entire scope of responsibilities.
For contract management specifically, Plexus delivers end-to-end lifecycle support from initial request through ongoing monitoring and renewal. The platform's AI capabilities automate routine tasks like contract review, metadata extraction, and risk analysis, whilst workflow automation ensures agreements move efficiently through drafting, negotiation, approval, and execution. This comprehensive approach addresses the reality that contracts don't exist in isolation—they're part of broader legal operations that require coordinated workflows, centralised knowledge, and integrated analytics.
Organisations implementing Plexus typically see 65% improvements in legal productivity, 90% faster contract execution times, and 70% reduction in routine administrative tasks. These efficiency gains enable legal teams to double their impact without increasing headcount, transforming legal from a bottleneck into a strategic enabler of business growth.
The platform's modular architecture means organisations can start with contract management and progressively add matter management, compliance tracking, or other capabilities as needs evolve. This scalability makes Plexus appropriate for mid-market companies managing hundreds of contracts annually as well as enterprises coordinating thousands of agreements across global operations.
Platform capabilities (with table)
Plexus provides comprehensive functionality across every stage of the contract lifecycle and beyond:
|
Capability area
|
Key features |
Business value
|
|
Intake & Triage
|
Structured request forms, automated routing, self-service templates, workload visibility
|
Eliminates ad-hoc requests, reduces legal bottlenecks, improves responsiveness
|
|
AI-Powered Drafting
|
Intelligent templates, clause libraries, automated population, playbook integration
|
60-80% reduction in drafting time, improved consistency, reduced risk
|
|
Collaboration & Review
|
Real-time collaboration, version control, AI risk analysis, clause-level feedback
|
Faster review cycles, better stakeholder coordination, enhanced risk identification
|
|
Workflow Automation
|
Configurable approvals, automated routing, escalation management, e-signature integration
|
70-90% faster approvals, eliminated bottlenecks, complete audit trails
|
|
AI Contract Analysis
|
Automated metadata extraction, obligation identification, risk scoring, intelligent search
|
Transforms contract data into strategic insights, proactive risk management
|
|
Repository & Access
|
Centralised storage, powerful search, role-based permissions, mobile access
|
Single source of truth, democratised access to contract knowledge
|
|
Obligation Management
|
Automated deadline tracking, proactive alerts, renewal workflows, performance monitoring
|
Prevents missed obligations, optimises renewals, ensures compliance
|
|
Analytics & Reporting
|
Portfolio dashboards, custom reports, cycle time analysis, spend tracking
|
Data-driven decision making, continuous process improvement, executive visibility
|
|
Integrations
|
Salesforce, Microsoft 365, DocuSign, ERP systems, procurement tools
|
Seamless workflows across business systems, eliminated data silos
|
The platform's AI capabilities extend beyond basic automation. Five key departments benefit from Plexus's comprehensive approach: legal teams gain efficiency and visibility, finance departments get better budget tracking and compliance monitoring, sales organisations accelerate deal cycles, procurement teams optimise supplier management, and marketing departments ensure brand protection and regulatory compliance.
Modular, scalable, future-proof
Plexus's modular architecture allows organisations to implement capabilities based on immediate priorities whilst maintaining flexibility to expand as needs evolve. Start with contract management to address urgent bottlenecks, then progressively add matter management for broader legal operations visibility, compliance tracking for regulatory requirements, or document automation for routine legal deliverables.
This modularity provides several strategic advantages. Organisations avoid paying for functionality they don't need immediately, implementation focuses on high-priority pain points that deliver quick wins, teams can learn the platform progressively rather than being overwhelmed, and the technology investment grows with your business rather than requiring replacement as needs change.
Plexus's AI capabilities continuously improve as the platform learns from your contract data, industry patterns, and user feedback. This means the system becomes more valuable over time rather than becoming obsolete like traditional software. Regular platform updates deliver new capabilities automatically, ensuring your organisation benefits from the latest innovations in AI and legal technology.
For growing organisations, this future-proof approach provides confidence that technology investments will support long-term business objectives. Rather than implementing point solutions that create new silos and integration challenges, Plexus provides unified infrastructure that scales efficiently whilst maintaining the flexibility to adapt as legal operations mature.
Book a Custom Demo with Plexus
See how Plexus transforms contract management for organisations like yours. Our team will demonstrate platform capabilities tailored to your specific pain points, discuss implementation approaches that fit your timeline and resources, provide ROI estimates based on your contract volumes and processes, and answer questions about pricing, integrations, and ongoing support.
Book your personalised demo to discover how AI-powered contract lifecycle management can help your legal team double their impact without increasing headcount.
Download the CLM Buyer's Guide
Making informed decisions about contract lifecycle management requires understanding key evaluation criteria, common implementation pitfalls, and realistic ROI expectations. Our comprehensive buyer's guide provides frameworks for assessing your organisation's needs, checklists for evaluating CLM vendors, questions to ask during vendor selection, and best practices from successful implementations.
Download the guide to ensure your CLM investment delivers maximum value for your organisation's contract management transformation.






.png?width=651&height=588&name=Untitled%20design%20(12).png)
-1.png?width=651&height=588&name=Untitled%20design%20(13)-1.png)

.png?width=651&height=588&name=Untitled%20design%20(16).png)
.png?width=600&height=160&name=CUSTOMER%20NEWS%20Archtop%20Fibers%20Digital%20Construction%20Success%20with%20Render%20(6).png)
